Computer Connections
This page attempts to explain the numerous types of connections used on computers. Shown below is a picture of the rear panel on a Mac mini with the ports labelled:
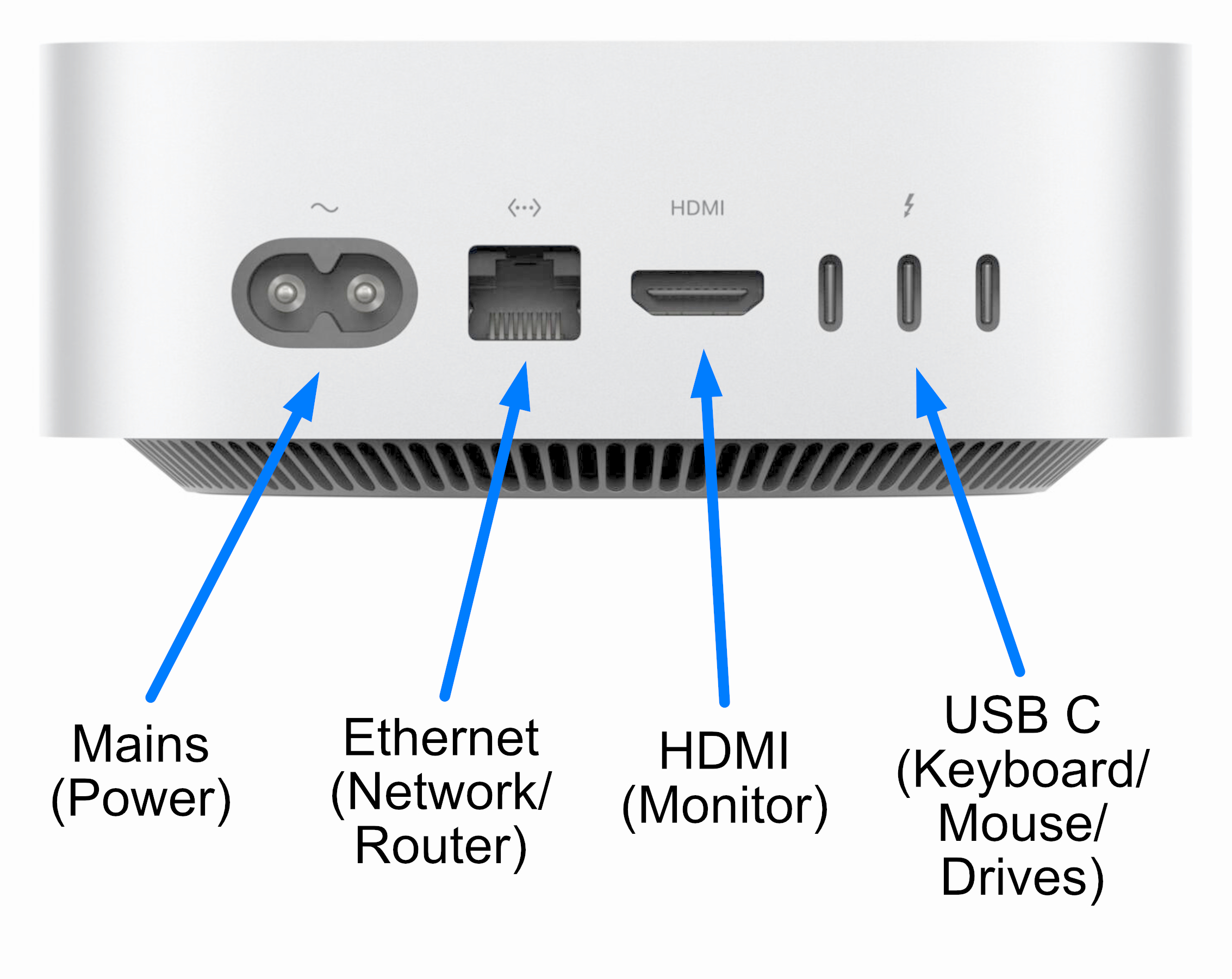
USB-C
In general a large number of different types of ports are disapearing to be replaced with just one connector, the USB-C. All USB-C ports are identical in shape, but the type of signals that they carried vary considerably. The shape of the connector allows the cable to be plugged in either way.
The European Union has stated that all mobile phones should now use USB-C, reducing waste by allowing phone chargers to be re-used when changing to a phone from another manufacturer. A large number of manufacturers now ship mobile phones without a charger, again to reduce waste as you can re-use the charger from your previous phone. As newer devices use USB-C, such as speakers, games consoles, battery packs, games controllers etc., it allows a single charger to be used to charge every device.
As well as power, a USB-C port can also support video and data. This is where is starts to get confusing, as some ports are power only, some also support USB (differing speeds), some also support ThunderBolt (differing speeds), and some can carry video (differing resolutions).
The other confusion comes when buying cables. Again some cables only support charging, most also support slower USB (USB 2), then better cables handle faster USB, Thunderbolt and/or video (2K, 4K, 8K).
For charging purposes, USB ports can increase their voltage when required. The charger/devices at each end of the cable have to agree what voltages are available/safe, and then the supply voltage and current can be increased. This allows a single USB C port and cable to be able to carry up to 240W to/from a device.
Some examples: A mobile phone USB-C port generally supports power in and out (around 30W), plus USB 2 (maybe USB 3 for faster devices), and possibly video. A USB-C port on a high end laptop will support higher power in (140W+), USB 4, Thunderbolt 5 and 4K video.
Video
The most common type of video connector is HDMI. This connector is standard on most TVs, set top boxes, Blu-Ray players etc.

HDMI
HDMI 1.4 supports 4K @ 30Hz, HDMI 2 supports 4K @ 60Hz, HDMI 2.1 and 2.2 support much higher resolutions

DisplayPort
Looks very similar to a HDMI connector. Not common on TVs, much more common on monitors. Can support some advanced display modes for gaming when paired with top end graphics cards and monitors.

USB C
The USB C port can also carry video. You can purchase USB C to HDMI or DisplayPort cables.
Older Style Connectors
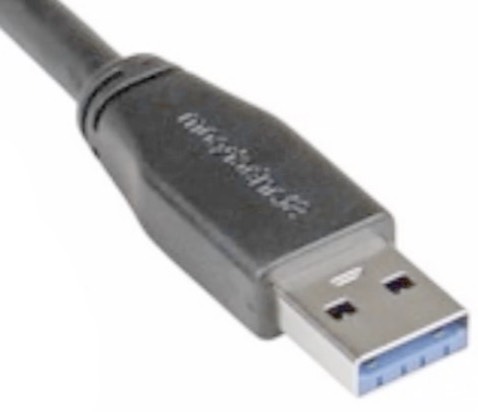

USB A
Was very common on computers but is rapidly being replaced with USB C. Generally used for wired mice and keyboards. Can carry data up to USB 3 speeds. Very common also in cars, airplanes, hotels etc. for charging purposes.
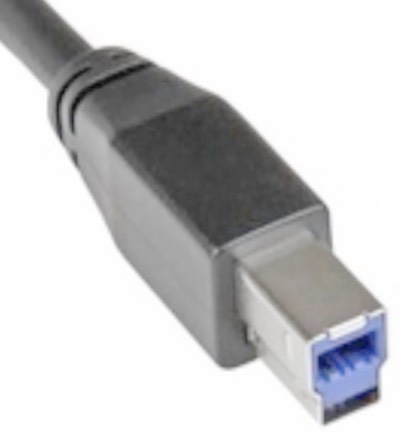

USB B
A variant on the USB A connector, normally seen on the back of devices such as printers and external hard drives.

USB Micro B
Commonly used on small devices such as older mobile phones, batteries, headphones etc. Normally for charging but can also carry slower speed data.
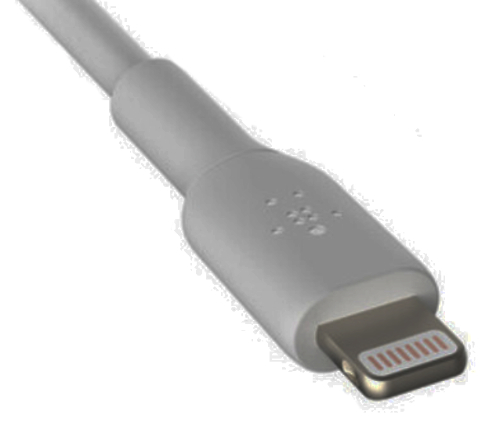

Lightning
Used on previous generation Apple iPhones, plus a number of other Apple devices such as keyboards, mice and remotes.